C Before E Except After I
crypto-bridge
Nov 27, 2025 · 14 min read
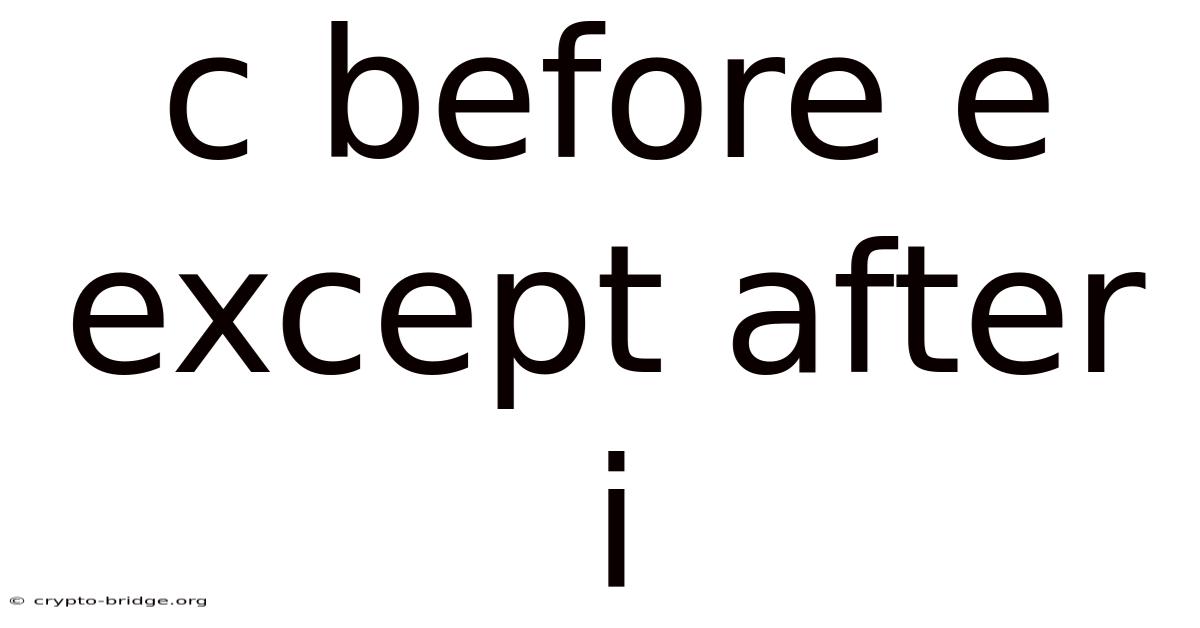
Table of Contents
Imagine sitting in elementary school, staring blankly at a spelling test. The word "receive" looms large, and you hesitate. Is it "ei" or "ie"? Then, a little voice in your head pipes up: "‘i’ before ‘e’ except after ‘c’!" A sigh of relief washes over you as you confidently fill in the letters. This simple rule, seemingly etched into the minds of English speakers everywhere, has guided countless writers through the treacherous waters of spelling.
But is it as reliable as we think? Like many rules of thumb in language, the "i before e except after c" rule has its limitations and exceptions. While it holds true in many cases, blindly following it can lead to some embarrassing spelling errors. So, let's dive deep into this famous rule, explore its origins, understand its exceptions, and ultimately, determine its usefulness in the age of spellcheck.
Main Subheading
The "i before e except after c" rule is a mnemonic device intended to help English speakers remember the correct spelling of words containing the ei or ie letter combinations. It's a staple in elementary education, designed to simplify the complexities of English orthography. The rule suggests that when these two vowels appear together, the correct order is generally ie, unless the preceding letter is c, in which case the order should be ei.
This rule is taught so pervasively because it captures a common pattern in English spelling, providing a straightforward guideline for learners. Its simplicity makes it easy to remember, and its applicability to a significant number of words makes it a valuable tool in a child's early writing education. However, the rule's exceptions and limitations are often downplayed, leading to confusion and frustration for those who rely on it too heavily. The English language, with its diverse historical influences and borrowed words, rarely adheres strictly to any single rule, and the "i before e except after c" rule is no exception. Recognizing the nuances and limitations of this rule is crucial for mastering English spelling.
Comprehensive Overview
The "i before e except after c" rule is more than just a quirky mnemonic; it reflects underlying patterns in the English language, though not without significant exceptions. To fully understand it, we need to examine its linguistic roots, its practical applications, and its inevitable shortcomings.
Origins and Linguistic Basis: The origins of the rule are somewhat murky, but it likely emerged as a simplified guideline to address common spelling errors. The English language is a melting pot of influences, drawing from Germanic, Romance, and other linguistic families. This diverse heritage has resulted in a complex and sometimes inconsistent spelling system. The "i before e" rule can be seen as an attempt to impose order on this chaos, providing a predictable pattern where irregularity often reigns.
The rule's effectiveness stems from the fact that many English words with ie and ei combinations are derived from French or Latin. In many of these words, the ie combination represents a single sound, while the ei combination often follows a c. However, this is not a universal pattern, and many exceptions arise from the diverse origins and evolution of English vocabulary.
Practical Applications: The primary purpose of the rule is to aid in spelling. It is particularly helpful for words where the ie or ei combination creates a single vowel sound, such as in "believe" (ie) or "receive" (ei). For many learners, the rule provides a quick and easy way to make an educated guess when faced with these spelling choices.
For example, consider the word "piece." According to the rule, since there is no c preceding the vowel combination, the order should be ie, which is correct. Similarly, in the word "deceive," the presence of c suggests that the order should be ei, which is also correct. These examples demonstrate the rule's usefulness in many common situations.
Exceptions and Limitations: Despite its widespread use, the "i before e except after c" rule is riddled with exceptions. These exceptions often arise from words of non-French or non-Latin origin, or from words where the vowel combination represents two distinct sounds rather than a single one. The existence of these exceptions significantly diminishes the rule's reliability.
One of the most common categories of exceptions includes words where the ei combination makes an /ā/ sound, as in "neighbor," "weigh," and "rein." These words often have Germanic origins, and their spelling patterns do not conform to the French or Latin-based logic of the rule.
Another category of exceptions includes words where the ie combination is not a single vowel sound, such as in "science," "society," and "diet." In these words, the ie represents two distinct vowel sounds, and the rule does not apply.
Furthermore, numerous other exceptions simply defy categorization. Words like "weird," "seize," "either," and "neither" do not follow the rule, and their spellings must be memorized individually. The sheer number of these exceptions makes the rule a less dependable guide than many learners initially believe.
The Role of Context: Even when the rule seems to apply, context can play a crucial role. For instance, the word "ceiling" follows the rule, but the word "ceilidh" (a Scottish or Irish social gathering) does not. Similarly, "receive" follows the rule, but "receipt" (though related) can be confusing for learners.
Understanding the context and etymology of a word can often provide clues to its correct spelling. However, this requires a deeper knowledge of language than the rule alone can provide.
Alternatives to the Rule: Given the limitations of the "i before e except after c" rule, it's important to consider alternative strategies for improving spelling skills. These strategies include:
- Memorization: For words that consistently defy the rule, rote memorization may be the most effective approach. Creating flashcards or using mnemonic devices specific to individual words can aid in this process.
- Phonetic Awareness: Understanding the relationship between sounds and letters can help in spelling. Breaking words down into their constituent sounds and identifying common spelling patterns can improve accuracy.
- Reading Extensively: Exposure to a wide range of written material is one of the best ways to improve spelling. By reading regularly, learners internalize common spelling patterns and develop a sense of what looks "right."
- Using Technology: Spell-checkers and grammar tools can be invaluable aids in identifying and correcting spelling errors. However, it's important to use these tools judiciously and not rely on them as a substitute for learning proper spelling.
- Understanding Etymology: Learning about the origins of words can provide insights into their spelling. Understanding that many English words are derived from French, Latin, or other languages can help explain why certain words are spelled the way they are.
In conclusion, while the "i before e except after c" rule can be a helpful starting point for learning English spelling, it is far from foolproof. A comprehensive approach that includes memorization, phonetic awareness, extensive reading, and the use of technology is essential for mastering the complexities of English orthography.
Trends and Latest Developments
In recent years, there has been a growing debate about the continued relevance of teaching the "i before e except after c" rule in schools. Some educators argue that the rule is too simplistic and misleading, given the numerous exceptions, and that it may be more effective to focus on teaching broader spelling patterns and strategies. Others maintain that the rule still has value as a basic guideline, particularly for young learners who are just beginning to grapple with the complexities of English spelling.
One emerging trend is the use of more nuanced and comprehensive spelling rules that take into account the etymology and phonetic structure of words. These rules are often more complex than the traditional "i before e" rule, but they can provide a more accurate and reliable guide to spelling. For example, some educators are teaching students about the influence of French and Latin on English spelling, and how this can help explain why certain words are spelled the way they are.
Another trend is the increasing reliance on technology to aid in spelling. Spell-checkers and grammar tools are now ubiquitous, and many people rely on them to catch spelling errors in their writing. While these tools can be helpful, they are not infallible, and they can sometimes make mistakes. It's important to use them judiciously and to develop a strong foundation in spelling skills.
Data from educational research suggests that a multi-faceted approach to spelling instruction is the most effective. This approach includes teaching basic spelling rules, but also emphasizing phonetic awareness, etymology, and extensive reading. It also involves providing students with ample opportunities to practice their spelling skills and to receive feedback on their work.
There's also a growing awareness of the importance of catering to different learning styles in spelling instruction. Some students may benefit from visual aids, such as flashcards or diagrams, while others may learn best through auditory methods, such as listening to recordings of words being spelled. Providing a variety of instructional methods can help to ensure that all students have the opportunity to succeed in spelling.
Professional insights from linguists and educators emphasize the need for a balanced approach to spelling instruction. While rules like "i before e except after c" can be useful as a starting point, they should not be treated as gospel. Instead, students should be encouraged to develop a broader understanding of the English language and to use a variety of strategies to improve their spelling skills.
Ultimately, the goal of spelling instruction should be to empower students to become confident and competent writers. This requires not only teaching them how to spell words correctly, but also helping them to develop a love of language and a desire to communicate effectively.
Tips and Expert Advice
Mastering English spelling, especially navigating the "i before e except after c" rule, requires a strategic approach that combines understanding the rule, recognizing its limitations, and employing effective learning techniques. Here are some expert tips to help you improve your spelling skills:
- Understand the Basics and the Exceptions: Begin by thoroughly understanding the "i before e except after c" rule. Recognize that while it's a helpful guideline, it's not a universal law. Make a list of common exceptions like "weird," "seize," "either," and "neither." Categorize these exceptions to better remember them. For instance, group words where ei makes an /ā/ sound, such as "neighbor" and "weigh." This structured approach can make the exceptions more manageable.
- Embrace Etymology: Delve into the origins of words. English is a blend of Germanic, Latin, and French influences, and understanding a word's etymology can provide clues to its spelling. For example, many words with ie or ei combinations have French or Latin roots. Researching the etymology can make spelling less arbitrary and more logical.
- Phonetic Awareness is Key: Develop a strong sense of phonetics. Understand how different sounds are represented by letters. Break words down into their constituent sounds and pay attention to common spelling patterns. This is particularly useful for words where the ie or ei combination represents distinct sounds, such as in "science" or "society."
- Read Widely and Actively: Immerse yourself in reading. Exposure to a wide variety of texts will naturally reinforce correct spelling. Pay attention to the spelling of words as you read, and make a note of any unfamiliar words. Actively engage with the text by highlighting or underlining words that you find challenging.
- Utilize Technology Wisely: Use spell-checkers and grammar tools as aids, not crutches. While these tools can catch errors, they won't teach you why a word is spelled a certain way. Use them to identify mistakes, but then take the time to understand the correct spelling and the reasons behind it.
- Create Personalized Mnemonic Devices: Develop your own mnemonic devices for challenging words. Mnemonic devices are memory aids that use associations to help you remember information. For example, you could remember the spelling of "piece" by thinking of "a piece of pie." The more personal and creative the mnemonic, the more effective it will be.
- Practice Regularly with Targeted Exercises: Engage in regular spelling practice. Use online quizzes, spelling games, and other interactive exercises to reinforce your learning. Focus on areas where you struggle the most. For example, if you consistently misspell words with ie or ei combinations, dedicate extra time to practicing those words.
- Keep a Spelling Journal: Maintain a spelling journal where you record new and challenging words. Write each word, its definition, and a sentence using the word. This active engagement with the word will help to solidify its spelling in your memory. Review your journal regularly to reinforce your learning.
- Seek Feedback and Collaboration: Ask for feedback on your writing. Have a friend, teacher, or colleague review your work and point out any spelling errors. Collaboration can also be helpful. Work with a study partner to quiz each other on spelling words and to discuss challenging spelling rules.
- Be Patient and Persistent: Mastering spelling takes time and effort. Don't get discouraged by occasional mistakes. Be patient with yourself, and keep practicing. The more you engage with the English language and the more strategies you employ, the better your spelling will become.
By combining a solid understanding of the "i before e except after c" rule with these expert tips, you can significantly improve your spelling skills and navigate the complexities of English orthography with greater confidence.
FAQ
Q: What exactly does the "i before e except after c" rule mean?
A: The rule is a mnemonic device to help remember the correct order of ie or ei in words. It suggests that ie generally comes before e, unless it follows the letter c, in which case ei is used.
Q: Is the "i before e except after c" rule always correct?
A: No, the rule has many exceptions and is not always reliable. It's best used as a general guideline rather than a strict rule.
Q: Can you give some examples of words that follow the "i before e except after c" rule?
A: Examples include "believe" (i before e) and "receive" (e before i after c).
Q: What are some common exceptions to the "i before e except after c" rule?
A: Common exceptions include "weird," "seize," "either," "neither," "neighbor," and "weigh."
Q: Why does the "i before e except after c" rule have so many exceptions?
A: The English language is derived from various sources, including Germanic, Latin, and French, each with its own spelling conventions. This mix leads to inconsistencies and exceptions.
Q: Should I still teach the "i before e except after c" rule to children?
A: While it can be a helpful starting point, it's crucial to also teach the exceptions and emphasize that it's not a universal rule. A more comprehensive approach to spelling instruction is recommended.
Q: Are there alternative strategies to improve spelling besides relying on this rule?
A: Yes, effective strategies include memorization, phonetic awareness, understanding etymology, extensive reading, and using technology as an aid.
Q: How can I remember the exceptions to the "i before e except after c" rule?
A: Use mnemonic devices, categorize exceptions by their phonetic patterns (e.g., ei making an /ā/ sound), and practice regularly with flashcards or quizzes.
Q: Is it better to rely on spell-checkers instead of learning spelling rules?
A: Spell-checkers are useful tools, but they should not replace learning proper spelling. Understanding spelling rules and patterns enhances writing skills and vocabulary.
Q: Where can I find more resources to improve my spelling?
A: There are numerous online resources, spelling books, and educational websites that offer exercises, quizzes, and explanations of spelling rules and patterns.
Conclusion
The journey through the "i before e except after c" rule reveals a fascinating glimpse into the complexities of the English language. While this mnemonic device has served as a helpful starting point for countless learners, its numerous exceptions highlight the importance of a more comprehensive approach to spelling. By understanding the origins of words, developing phonetic awareness, and employing effective learning strategies, one can navigate the intricacies of English orthography with greater confidence and accuracy.
Ultimately, mastering spelling involves more than just memorizing rules; it requires a deep engagement with language and a commitment to continuous learning. So, embrace the challenge, explore the nuances, and let the "i before e except after c" rule be a stepping stone on your path to becoming a more skilled and articulate writer. Now, take what you've learned and put it into practice! Share this article with fellow writers or language enthusiasts, and start a conversation about the quirks and challenges of English spelling. What are your favorite spelling tips and tricks?
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Dnd How Long Do Elves Live
Nov 27, 2025
-
How Do You Block A Website From Your Computer
Nov 27, 2025
-
How To Switch To Creator Account On Tiktok
Nov 27, 2025
-
What Does It Mean When You Dream Of Fighting
Nov 27, 2025
-
What Is Micro Nutrients In Plants
Nov 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about C Before E Except After I . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.