Molecular Mass Of Ca No3 2
crypto-bridge
Nov 28, 2025 · 9 min read
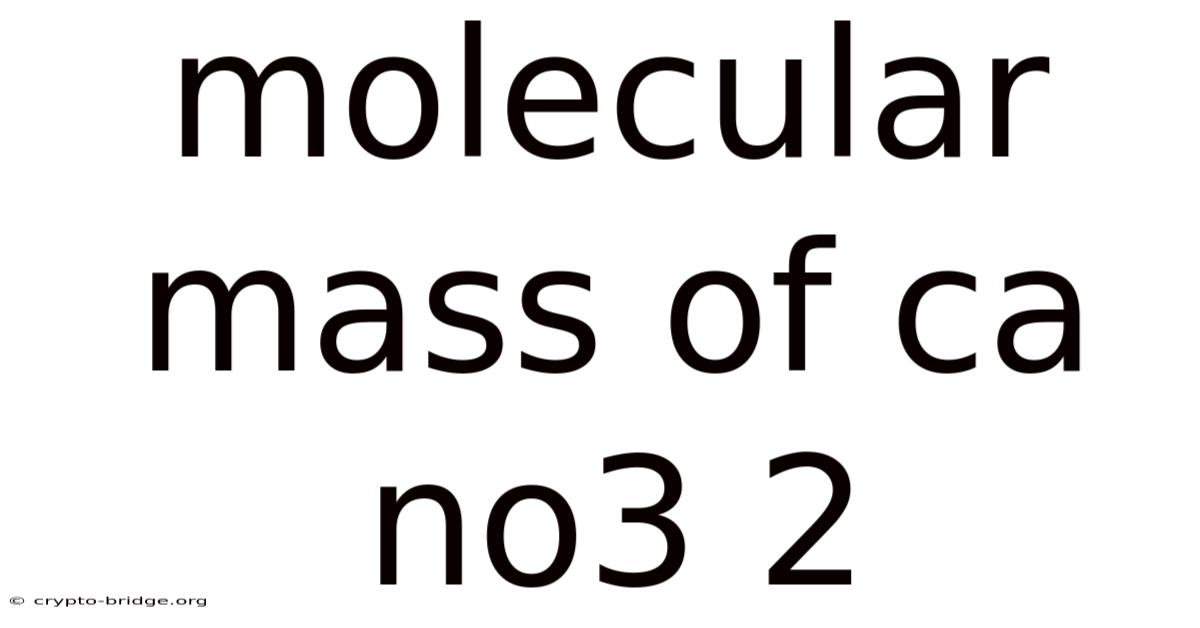
Table of Contents
Imagine you're in a chemistry lab, carefully weighing out a compound for a crucial experiment. Precision is key; a slight miscalculation could throw everything off. To achieve this accuracy, understanding the molecular mass of the compounds you're working with is paramount. It's not just a theoretical concept, but a practical necessity that bridges the gap between the microscopic world of atoms and the macroscopic world of measurable quantities.
Similarly, picture a farmer calculating the precise amount of fertilizer needed to nourish their crops. Too little, and the plants won't thrive; too much, and the environment suffers. Calcium nitrate, a common fertilizer, plays a vital role here. But to use it effectively, the farmer needs to know the molecular mass of Ca(NO3)2, ensuring they're applying the correct amount for optimal growth and minimal waste. This illustrates how molecular mass extends beyond the laboratory, influencing real-world applications in agriculture, medicine, and various other fields.
Unveiling the Molecular Mass of Calcium Nitrate: A Comprehensive Guide
The molecular mass of Ca(NO3)2, or calcium nitrate, is a fundamental concept in chemistry that allows us to understand the quantitative composition of this important compound. It represents the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a single molecule of calcium nitrate. This value is crucial for a multitude of applications, ranging from calculating molar concentrations in solutions to determining the stoichiometry of chemical reactions involving calcium nitrate.
Calcium nitrate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca(NO3)2. It's an ionic salt composed of a calcium cation (Ca2+) and two nitrate anions (NO3-). At room temperature, it exists as a white, crystalline solid. Calcium nitrate is highly soluble in water and is commonly encountered as a tetrahydrate, Ca(NO3)2·4H2O. This means that each formula unit of calcium nitrate is associated with four molecules of water. This compound finds widespread use as a fertilizer, providing plants with essential nutrients like nitrogen and calcium. It also has applications in wastewater treatment and as a component in some concrete mixes.
Comprehensive Overview
To truly grasp the significance of the molecular mass of Ca(NO3)2, it's essential to delve into the underlying principles. The molecular mass, often expressed in atomic mass units (amu) or grams per mole (g/mol), is calculated by summing the atomic masses of each element present in the chemical formula, multiplied by the number of atoms of that element. These atomic masses are readily available on the periodic table, and are determined experimentally using mass spectrometry.
Let's break down the process for calcium nitrate, Ca(NO3)2:
- Identify the elements: Calcium (Ca), Nitrogen (N), and Oxygen (O).
- Find the atomic masses:
- Calcium (Ca): approximately 40.08 amu
- Nitrogen (N): approximately 14.01 amu
- Oxygen (O): approximately 16.00 amu
- Count the atoms: In Ca(NO3)2, there is:
- 1 Calcium atom
- 2 Nitrogen atoms (inside the parentheses, the subscript 2 applies to the entire nitrate group)
- 6 Oxygen atoms (3 oxygen atoms in each nitrate group, multiplied by 2)
- Calculate the molecular mass: (1 x 40.08 amu) + (2 x 14.01 amu) + (6 x 16.00 amu) = 40.08 + 28.02 + 96.00 = 164.10 amu
Therefore, the molecular mass of anhydrous calcium nitrate, Ca(NO3)2, is approximately 164.10 amu.
However, as mentioned earlier, calcium nitrate is often found as a tetrahydrate, Ca(NO3)2·4H2O. To calculate the molecular mass of the tetrahydrate, we need to include the mass of the four water molecules:
- Molecular mass of water (H2O): (2 x 1.01 amu) + (1 x 16.00 amu) = 18.02 amu
- Molecular mass of 4 water molecules: 4 x 18.02 amu = 72.08 amu
- Molecular mass of Ca(NO3)2·4H2O: 164.10 amu + 72.08 amu = 236.18 amu
Thus, the molecular mass of calcium nitrate tetrahydrate is approximately 236.18 amu.
The concept of the mole is inextricably linked to molecular mass. A mole is defined as the amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.) as there are atoms in 12 grams of carbon-12. This number, known as Avogadro's number, is approximately 6.022 x 10^23. The molar mass of a compound is numerically equal to its molecular mass, but expressed in grams per mole (g/mol). Therefore, the molar mass of Ca(NO3)2 is 164.10 g/mol, and the molar mass of Ca(NO3)2·4H2O is 236.18 g/mol.
Knowing the molar mass is crucial for converting between mass and moles. For example, if you have 50 grams of anhydrous calcium nitrate, you can calculate the number of moles using the formula:
Moles = Mass / Molar Mass
Moles of Ca(NO3)2 = 50 g / 164.10 g/mol ≈ 0.305 moles
Trends and Latest Developments
While the molecular mass of Ca(NO3)2 itself is a well-established constant, research and development continue to focus on optimizing its production, application, and environmental impact. One key trend is the development of more efficient and sustainable methods for producing calcium nitrate fertilizers. Traditional methods can be energy-intensive and generate significant amounts of waste. Newer processes aim to reduce these environmental burdens by utilizing alternative raw materials and minimizing energy consumption.
Another area of active research is the development of controlled-release formulations of calcium nitrate fertilizers. These formulations are designed to release nutrients gradually over time, reducing nutrient loss through leaching and runoff. This not only improves the efficiency of fertilizer use but also minimizes the potential for water pollution.
The increasing awareness of the environmental impact of nitrogen fertilizers, including calcium nitrate, is driving research into more sustainable agricultural practices. This includes optimizing fertilizer application rates based on soil testing and crop needs, as well as exploring alternative nitrogen sources such as biological nitrogen fixation.
Furthermore, the use of calcium nitrate is expanding beyond traditional agriculture. It's finding increasing applications in wastewater treatment for odor control and corrosion prevention, as well as in the construction industry as a concrete additive to accelerate setting time and improve strength. These emerging applications are driving the development of new formulations and technologies tailored to specific needs.
Tips and Expert Advice
Using calcium nitrate effectively and safely requires careful consideration and attention to detail. Here are some practical tips and expert advice:
-
Understand the difference between anhydrous and hydrated forms: As we've discussed, calcium nitrate can exist in anhydrous (without water) and hydrated forms. Always check the label to determine which form you're using and adjust your calculations accordingly. Using the wrong molar mass can lead to significant errors in your application rates.
-
Calculate application rates accurately: Whether you're using calcium nitrate as a fertilizer or in another application, it's crucial to calculate the correct application rate. Over-application can lead to nutrient imbalances, environmental pollution, and economic waste. Soil testing and crop needs assessments can help you determine the optimal application rate for your specific situation.
-
Consider soil pH: Soil pH affects the availability of nutrients to plants. Calcium nitrate is most effective when the soil pH is within the optimal range for the crop being grown. If the soil pH is too high or too low, nutrients may become locked up and unavailable to plants, even if you've applied the correct amount of fertilizer.
-
Store calcium nitrate properly: Calcium nitrate is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the air. This can cause it to cake or clump, making it difficult to handle and apply. Store calcium nitrate in a cool, dry place in a tightly sealed container to prevent moisture absorption.
-
Handle calcium nitrate safely: While calcium nitrate is not highly toxic, it can be irritating to the skin and eyes. Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and safety glasses, when handling calcium nitrate. Avoid inhaling dust or fumes.
-
Be aware of potential interactions: Calcium nitrate can interact with other chemicals, potentially forming undesirable compounds or reducing its effectiveness. Avoid mixing calcium nitrate with incompatible materials, such as strong acids or bases. Always consult a compatibility chart or seek expert advice before mixing calcium nitrate with other chemicals.
By following these tips and seeking expert advice when needed, you can use calcium nitrate effectively and safely, maximizing its benefits while minimizing its potential risks.
FAQ
Q: What is the chemical formula for calcium nitrate? A: The chemical formula for calcium nitrate is Ca(NO3)2.
Q: What is the molecular mass of anhydrous calcium nitrate? A: The molecular mass of anhydrous calcium nitrate (Ca(NO3)2) is approximately 164.10 amu.
Q: What is the molecular mass of calcium nitrate tetrahydrate? A: The molecular mass of calcium nitrate tetrahydrate (Ca(NO3)2·4H2O) is approximately 236.18 amu.
Q: What is the molar mass of calcium nitrate? A: The molar mass of anhydrous calcium nitrate is 164.10 g/mol, and the molar mass of calcium nitrate tetrahydrate is 236.18 g/mol.
Q: How is the molecular mass of a compound calculated? A: The molecular mass of a compound is calculated by summing the atomic masses of each element present in the chemical formula, multiplied by the number of atoms of that element.
Q: Why is knowing the molecular mass of calcium nitrate important? A: Knowing the molecular mass of calcium nitrate is crucial for calculating molar concentrations in solutions, determining the stoichiometry of chemical reactions, and accurately applying it as a fertilizer.
Conclusion
Understanding the molecular mass of Ca(NO3)2, both in its anhydrous and hydrated forms, is more than just an academic exercise. It's a practical skill with far-reaching implications. From ensuring precision in chemical experiments to optimizing fertilizer application in agriculture, this knowledge empowers us to work effectively and responsibly with this important compound.
By grasping the fundamental principles behind molecular mass calculations, staying abreast of the latest developments in calcium nitrate production and application, and following expert advice for safe and effective use, you can unlock the full potential of this versatile chemical. Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of calcium nitrate, we encourage you to share this knowledge with others and explore its diverse applications in your own field. Leave a comment below with your thoughts or questions, and let's continue the conversation!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Where Is Tracy Edwards Now 2022
Nov 28, 2025
-
Best Over The Counter Ear Infection Medicine For Dogs
Nov 28, 2025
-
What Does It Mean When A Cardinal Visits
Nov 28, 2025
-
Is The Solar Tax Credit Refundable
Nov 28, 2025
-
Man From Princess And The Frog
Nov 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Molecular Mass Of Ca No3 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.